Jason Bowes, the COO of CloudNC, took some time to tell us about CloudNC’s journey starting from 2015 when AI was still a fully unmapped territory.
CAM Doesn’t Cut It
What problem did you set out to solve?
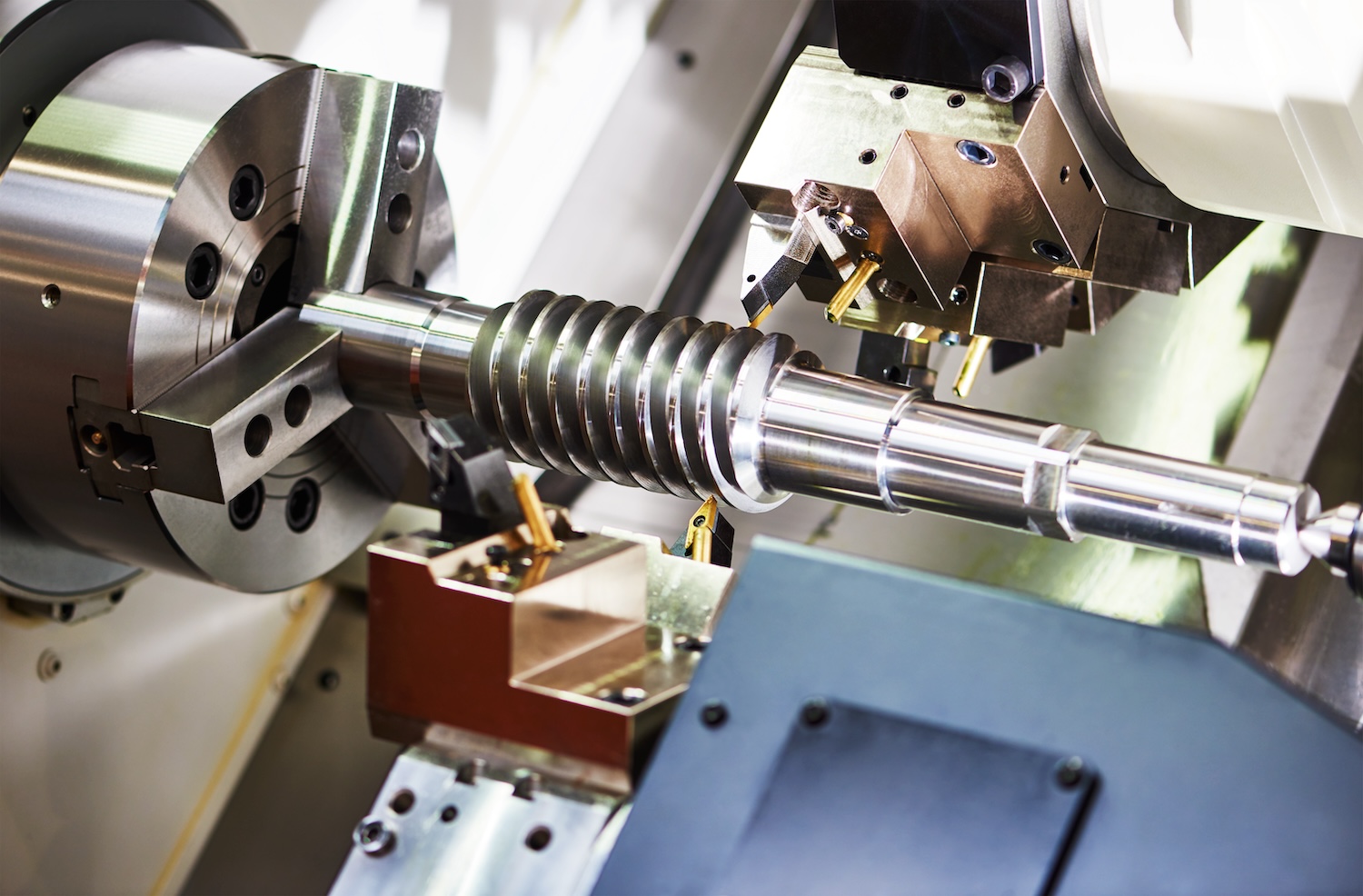
Precision machining is fundamental to modern life, as the metal components it makes are used throughout every industry and sector. But it’s not automatic – processes like programming are carried out manually by experts, and require considerable time, effort and resources to execute.
For example, to produce a component, an operator uploads a model and manually codes a CNC machine to make it. But that process is a bottleneck: CNC machines are difficult to use, and the software is often complicated and non-intuitive. In addition, the machines can be programmed in a near-infinite number of ways, depending on the complexity of the part, the materials and tools being used, and the skill of the operator.
This creates a huge disparity in efficiency and reliability across the machining sector. Expert machinists can come up with solutions that improve delivery, but until now computers have until now been unable to match them – the calculation is too big to brute force. We wanted to solve this problem.
Why does CAM need an “assistant”? Why can’t existing systems do this?
Traditional CAM systems are powerful, but they’re tools – not assistants. They rely on the user to make thousands of small, context-dependent decisions: which operations to use, how to order them, which tools to pick, what feeds and speeds to apply. There are templates and feature-recognition add-ons, but they’re rule-based – brittle, hard to scale, and reliant on expert setup, and they don’t meet the needs of many machine shops.
CAM Assist is different. It uses AI to assess the whole part and then suggest a working toolpath strategy that works for around 80% of all 3+2 axis components. It can then make those same choices in seconds. It’s not about replacing the human – it’s about removing the rote work and accelerating them so they can focus on what really matters, and where their expertise makes a difference.
Automated G Code with Human Control
So what does CAM Assist actually do?
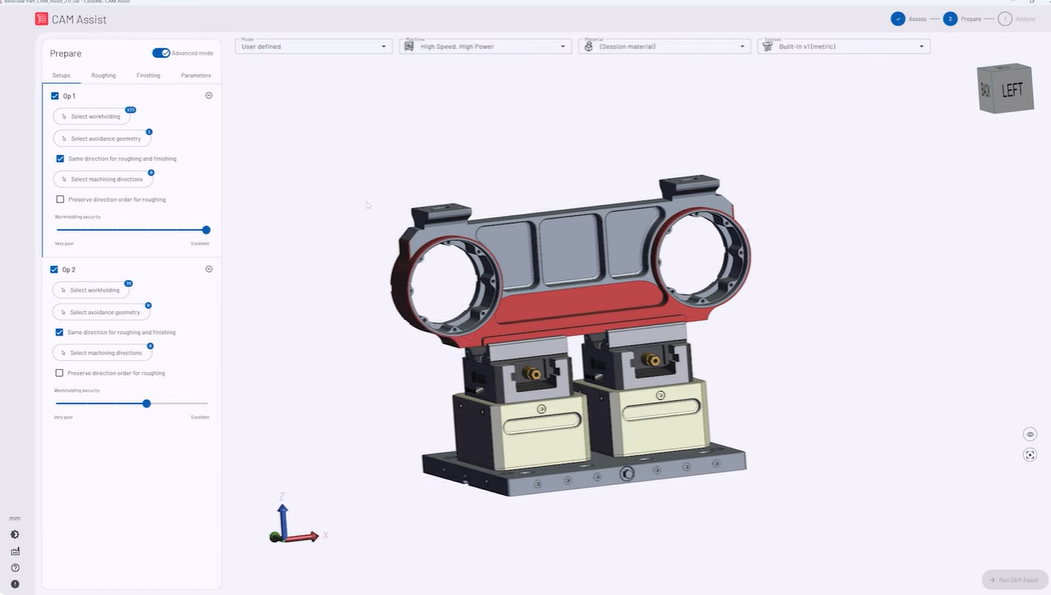
CAM Assist is a plug-in for CAM software that generates professional machining strategies in seconds at the click of a button.

As a result, the amount of time it takes to program a CNC machine to make a component is greatly reduced, enabling manufacturers using CAM Assist to raise productivity and shorten lead time.. The software expedites estimating, frees up time for experienced programmers, and also allows junior employees to program more complex parts.
What does the process from CAD file to the machinist pushing the start button look like?
A CAM Assist user uploads a 3D model of a 3-axis or 3+2 axis prismatic part into their CAM package, defines the setups and presses the CAM Assist button. The software then determines the milling tools needed from those available and how they will be used.
In minutes or seconds, depending on part complexity, CAM Assist drafts the code required to instruct a CNC machine how to make it, within the user’s existing CAM program. The programmer can then check that code, amend as much or as little as they like, and press start.
What happens if there are Design for Manufacturing issues?
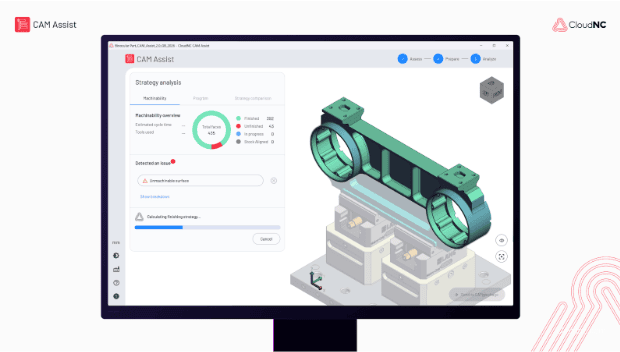
CAM Assist flags geometry that’s potentially unmachinable or inefficient to machine – things like unreachable corners, deep pockets, or areas needing special tooling. It doesn’t automatically redesign the part (yet!), but it helps the machinist or designer understand where trouble might occur before hitting cycle start.
You recently launched CAM Assist 2.0. What changed?
CAM Assist 2.0 builds on the speed of CAM Assist v1, but layers on the oversight, feedback and shared intelligence machine shops need to use AI with confidence.

Previously, when asked to generate a toolpath, CAM Assist would carry out its work and present the user with its solution. However, that might mean that the programmer would have to understand and unpick an extremely complex operation in order to understand the AI’s working, in effect changing the user’s role from creator to editor.
CAM Assist 2.0 gives control back to the programmer by enabling them to understand the AI’s working as it generates a strategy or operation. As a result, programmers stay firmly in control of every critical decision.
New Part, New Code – Creating a Bottleneck
What’s the biggest value CAM Assist delivers?
It makes machinists more productive and efficient. Many users report their programming time for a part is cut substantially, in that parts that would usually take several hours to program now can take just minutes.
You launched around two years ago. How’s the reception been?
It’s been very positive – we’ve gone from zero to CAM Assist now in use in over 1,000 machine shops worldwide, with some machine shops using it daily to become faster and more efficient.
We’ve also developed close relationships with many customers too, which has helped us resolve some initial obstacles – in particular, how to integrate different tool libraries effectively with the AI – and they’re now feeding back what they want from the software, which also helped shape our new 2.0 update.
Who’s benefiting the most today?
Right now, small to medium-sized machine shops see the fastest wins – especially those with high-mix volume and lots of new parts, and where programming time is a bottleneck.
Any user stories you can share?
One US customer told us that CAM Assist reduced the time that it took to program a part from 1.5-2 hours, down to 23 minutes – including fine-tuning time – and they were replicating similar efficiency gains across their operations. We’re also seeing customers being able to turnaround quotes much more quickly – often in half the time – which is helping them win more work; a vital asset when the sector is changing rapidly as work is reshored.
What programs do you integrate with?
CAM Assist currently integrates with many leading CAM packages, including Autodesk Fusion, Mastercam, Siemens NX, Solidcam, Creo and GibbsCAM, with more integrations planned very very soon. Our goal is to bring this capability wherever machinists already work so that as many people as possible can benefit.
How are you priced?
We use a subscription model based on seats and company type. Pricing scales with the number of users and machines, so it’s accessible for small shops but can also support enterprise rollouts. We also offer a moneyback guarantee if for some reason the software isn’t a fit.
AI Moving from Hype to Practical Impact
CloudNC started before the recent AI wave. What’s different now?
We’ve been at this since 2015 – long before “AI startup” became a buzzword! One big difference is the dataset – there is no big database of how exactly CNC machines behave, so we had in part to build that ourselves through owning our own factory. That means our algorithms are grounded in real chips, not just theory – which is critically important when applying an AI to a machine that costs tens of thousands of dollars.
Where is the industrial AI space going?
We’re finally seeing AI move from hype to practical impact. In manufacturing, that means systems that truly assist and make users faster – not just us, but companies like MachineMetrics, Paperless Parts, and others.
The next few years will bring AI that links the whole chain: design, CAM, scheduling, QA, and quoting – each step informing the next. A lot of companies are working on pieces of that puzzle, and that’s great for the ecosystem.
And where is CloudNC going?
While CAM Assist has a huge potential market, it is also just the start. Our mission to transform global manufacturing with AI – right now, that means making programmers much more productive with the help of CAM Assist. But long-term that means using this technology to tackle adjacent problems, like quoting, scheduling, design for manufacturing, and maybe beyond.
 Europe
Europe  Türkiye
Türkiye  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Global
Global 

 Login with my Xometry account
Login with my Xometry account  0
0







Comment(0)