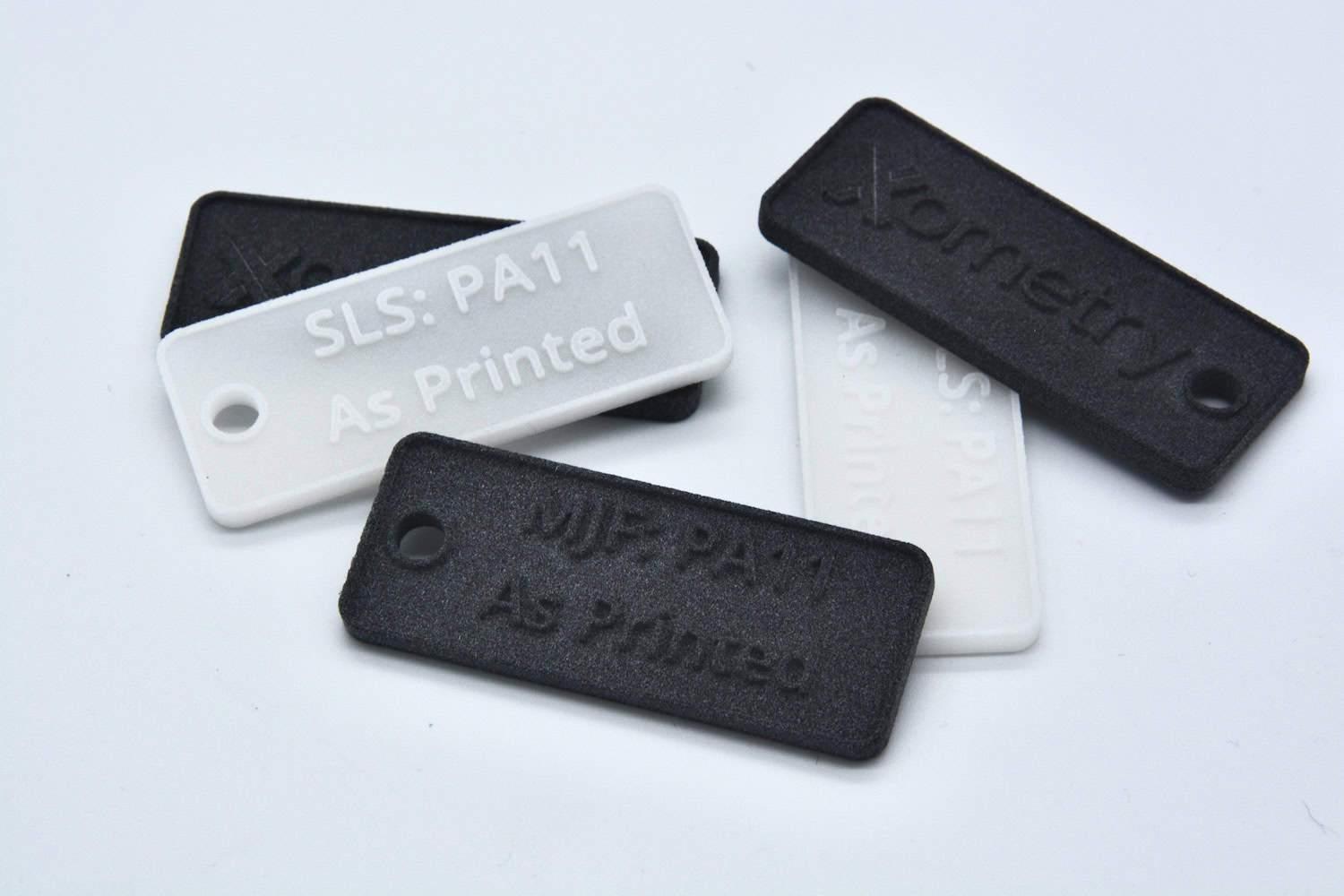
When designing products or their elements one of the essential features can be color. Among other advantages, 3D printing can be effective when you need to manufacture parts of different colors. This article will overview two possible options to get your 3D printed parts in color: direct color 3D printing and post-processing that will make your parts colored.
Two 3D Printing Coloring Methods
There are two most popular ways to get colorful 3D prints:
- Get parts directly printed in color: using the print material (powder or filament) of desired color
- Get parts post-processed: for example, you can use standard color material (Grey/White) and dye it with desired color
Types of Color 3D Printing
Direct 3D Printing
Direct color 3D printing uses a colorful filament to 3D print your models. For example, FDM is the most popular 3D printing technology that can use colorful filaments. Bright colors and nice details can be achieved depending on the quality of the filament. The main drawback with direct color 3D printing is, it won’t allow you to mix the colors, so you can’t choose any RAL color with the standard solutions.
Indirect 3D printing
Indirect color 3D printing applies the color from an external source during the printing process (e.g in Multi Jet Fusion 3D printing). This technology is much more precise and allows for a more realistic appearance of the 3D prints. It is important for you to remember that indirect color 3D printing uses CMYK color mode and you need to take that into consideration when preparing your model.
Color 3D Printing Options Available at Xometry
Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) and Fused deposition modeling (FDM) are the two popular color 3D printing technologies.
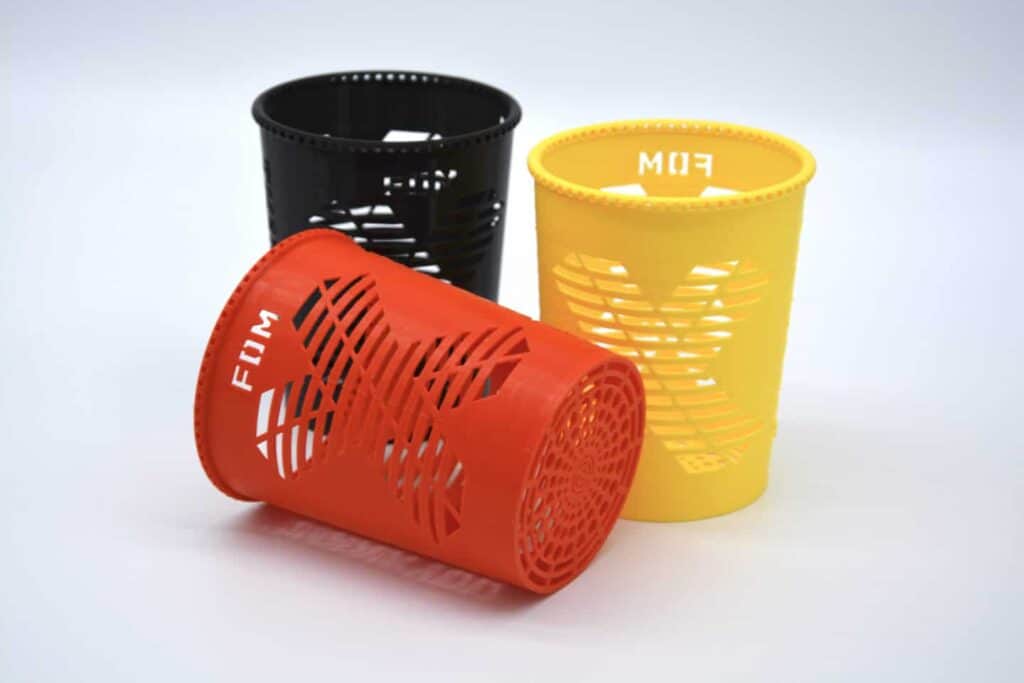
Color fused deposition modeling (FDM)
FDM is one of the most commonly used 3D printing technologies on the market FDM parts are available in a wide range of colors (Black, Blue, Grey, Ivory, Red) in the most common materials like ABS and ASA.
When 3D printing multi-colored parts using FDM you must use the same material throughout the entire part. For example, you cannot go from printing in white ASA to black ABS. Generally, common materials like ASA, PLA and ABS come in a wide selection of colors. In order to get a multi-colored part, split the CAD model into parts of different colors and assemble them later.
Advantages:
- Achieves bright colors and nice details
- Good mechanical properties
Disadvantages:
- Monotonous colors (e.g Lego blocks) and not as precise as MJF color printing
- Mixing of colors is not possible

Color Multi Jet Fusion (MJF)
Multi-Jet Fusion is the only technology that can print engineering-grade plastics (Polyamide (Nylon 12)) in full color. With this technology, you can produce full-color functional parts while maintaining optimal mechanical properties. Since it is indirect 3D printing, it is capable of creating full-spectrum color parts with a voxel-control system and is much accurate with color reproduction.
Advantages:
- Mechanically strong – can be used for end-use parts
- Cost-efficient, especially with small and mid-sized series
- High productivity – can be used for batch production
- This technology is much more precise and allows for a more realistic appearance of the 3D prints
Disadvantages:
- Transparencies not possible
- Not suitable for very small, delicate parts

Post-processing Options for Coloring
If a filament or powder of the desired color is not available or the technology you want to use doesn’t offer a color print material, coloring at post-processing is an option.
Spray Painting
As the name indicates, spray painting is the coating of paint on the 3D part using spray paint cans and a very common coloring technique that is used even for conventionally machined parts. One major drawback is, the paint coating is just on the surface level; it doesn’t go deeper into the part and hence, if it is scratched or subjected to wear and tear, the internal natural color is visible.
Technologies compatible: MJF, SLS, SLA, FDM

Dyeing
Unlike spray painting, which coats the paint only on the surface of the part, dyeing colors the plastic deeply. This assures vibrant colors in particular and also makes it possible to avoid the phenomenon of peeling or scratching which can occur with spray paint. The lack of excess thickness prevents loss of detail, thus conforming most closely to the original design. This quality is critical and most important when 3D printing technology has been selected because of the design complexity. Many users prefer dyeing a part in black due to its uniformity in color and its overall look.
Technologies compatible: MJF, SLS
How to Prepare Your Design for Color 3D Printing?
Not all file formats for 3D printing, like .stl, .catpart, contain information on the desired colors. If you want to print your model with color, especially with MJF, we advise you to create and upload an additional .obj file with color texture specifications, while calculating the costs. Whereas with FDM, any file format works as the filament itself is colored.
Conclusion
As you can see, there are 2 approaches to get colorful 3D prints: produce them with the technologies that allow to add color during the 3D printing process (FDM, MJF) or post-process them with dyeing or spray painting. Both options are cost-effective and usually don’t substantially increase the cost of the 3D prints (on average by 10-15%). Check out the available color options, prices, and lead times by uploading your CAD files to the Xometry Instant Quoting Engine®.
 Europe
Europe  Türkiye
Türkiye  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Global
Global 

 Login with my Xometry account
Login with my Xometry account  0
0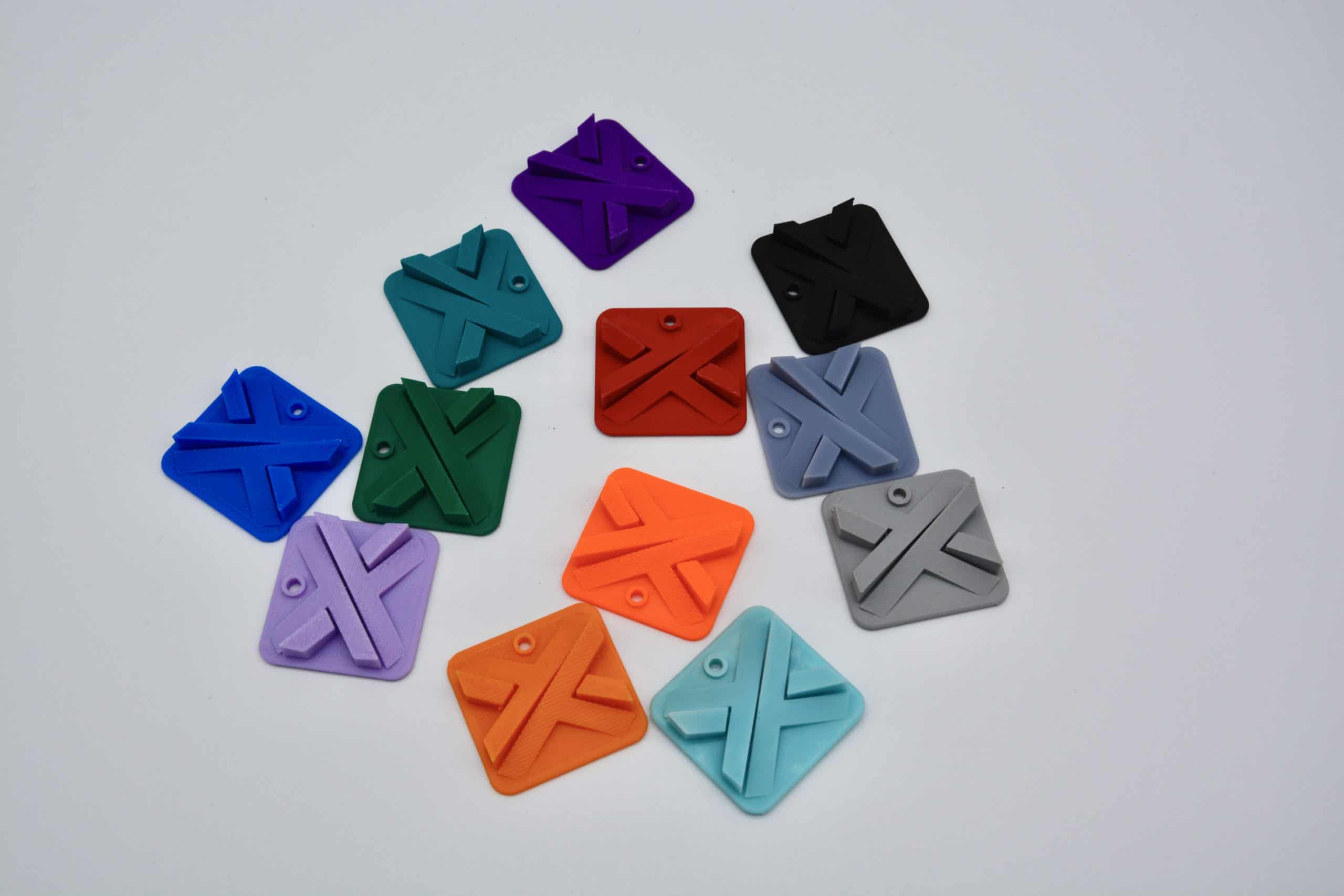






 Download
Download