When it comes to finishing options for aluminium parts, the choices can be baffling. Two standout methods, powder coating and anodizing, often find themselves at the centre of the debate. But what exactly sets them apart?
Whether in the automotive industry, aviation, or just curious, understanding these methods will equip you with the knowledge to choose your specific needs.
What is Powder Coating?
Powder coating is a finishing technique where a dry, free-flowing powder is applied to a surface, typically aluminium, with a spray gun. The powder adheres to the metal surface through electrostatic application before being cured under heat, forming a tough, uniform layer.

Benefits and Key Features
- Durability: A powder coat creates a hard finish that’s more resistant to scratching, chipping, and corrosion than traditional paints
- Variety: Many colours and textures are available, offering great versatility
- Cost-effective: Though the initial setup may be expensive, the long-term benefits make it cost-efficient
- Environmentally friendly: This process emits few volatile organic compounds (VOCs), making it a greener choice
Common Applications
- Used for coating wheels, bumpers, and other parts for enhanced aesthetics and protection
- Found in appliances and gadgets for a sleek, durable finish
- It is ideal for coating window frames, railings, and other building elements

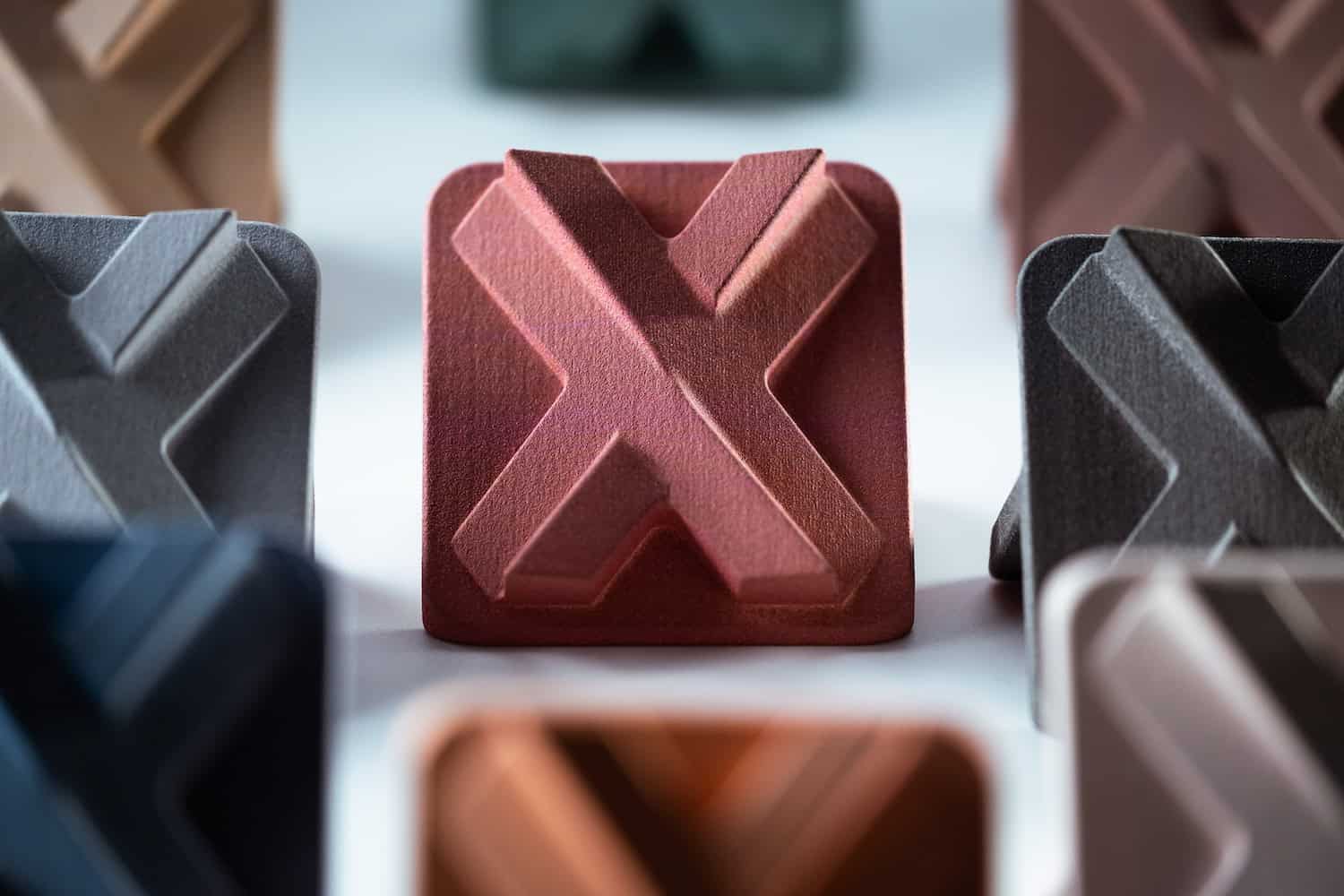
What is Anodizing?
Anodizing is an electrolytic process that forms a protective oxide layer on the surface of aluminium. A robust, corrosion-resistant layer is created by submerging the aluminium in an acid electrolytic bath and passing an electric current through it. This natural oxide layer is not merely a coating but is integrated with the underlying aluminium, providing a strong bond.

Benefits and Key Features
- Strength and durability: Unlike other coatings, anodized aluminium doesn’t peel or chip, offering lasting protection
- Aesthetic flexibility: Anodizing allows for colouring and decorative finishes, providing a broad palette of options
- Enhanced adhesion: The process allows for better adhesion for paints and glues.
- Non-toxic: The process uses non-hazardous materials and is generally considered more environmentally friendly
Common Applications
- Anodizing is vital in aviation, where weight and durability are key considerations
- Used in surgical instruments and other medical devices due to its resistance to wear and biological contamination
- Kitchen utensils and cookware often utilise anodizing for a smooth, non-reactive surface

Powder Coating and Anodizing Comparison
Cost
When evaluating cost, several factors come into play. Powder coating often has higher initial equipment and setup costs. Still, it can be more cost-effective in the long run, particularly for large-scale projects.
On the other hand, anodizing typically has lower entry costs but may be more expensive for custom colours and finishes. Ultimately, the price will depend on the specific requirements and scale of the project.
Durability
Durability is a vital consideration in choosing a surface treatment. Powder coating provides a robust surface that’s resistant to chipping and scratching. Its uniform coating ensures all-around protection.
Anodizing, however, takes it further by integrating the protective layer into the aluminium. This results in a finish that doesn’t peel or chip, offering long-term resilience. Both methods are highly durable, but anodizing may provide a slight edge regarding wear resistance.
Corrosion Resistance
Both powder coating and anodizing offer substantial protection in terms of corrosion resistance. A powder coat forms a sealed, continuous layer that prevents oxidation and corrosion.
By creating a thick oxide layer, anodizing also offers robust corrosion resistance. While both methods are highly effective, anodizing’s integrated oxide layer might provide more consistent and long-lasting protection against corrosion, especially in aggressive environments.
Comparison Table
| Characteristics | Anodizing | Powder Coating |
| Type | Electrochemical process | Electrostatic process |
| Cost | High | Moderate |
| Durability | Excellent | Good |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Colour Options | Limited colours | Wide range of colours |
| Surface Finish | Matte or satin texture | Glossy, matt, or satin textures |
| Colour Fading Resistance | Poor | Excellent |
| Eco-friendliness | Good | Excellent |
Application-Specific Considerations
Architectural Applications
When it comes to architectural applications, both powder coating and anodizing have their merits. Powder coating’s wide range of colours and textures makes it versatile for adding an aesthetic touch to window frames, railings, and other architectural elements.
On the other hand, anodizing offers a unique advantage with its corrosion-resistant properties. This makes it particularly suitable for structures in coastal areas where the salty air can accelerate corrosion.
Anodizing might lead in this context, providing enhanced protection against the elements.
Consumer Electronics
In the realm of consumer electronics, the coating process shines. Its sleek and attractive finish enhances the aesthetics of gadgets. At the same time, its scratch-resistant nature ensures that everyday wear and tear don’t mar its appearance.
The versatility in colours and textures allows manufacturers to match the finish with the product’s design. While robust, anodizing might not offer the same array of customisation options as powder coating, making powder coating the preferred choice for consumer electronics.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, both powder coating and anodizing find their niches. Powder coating’s durability makes it popular for coating wheels, bumpers, and other metal products that withstand harsh road conditions.
On the other hand, anodizing’s corrosion resistance makes it valuable in areas where vehicles might be exposed to corrosive elements, such as road salt. The choice here might depend on whether durability or corrosion resistance is the higher priority.
Aviation and Aerospace Applications
For aviation and aerospace applications, the corrosion-resistant properties of anodized aluminium shine. In an industry where weight, durability, and corrosion resistance are paramount, anodizing’s ability to provide all three qualities makes it a top choice.
The protective oxide layer helps extend the lifespan of crucial components, ensuring the safety and performance of aircraft.
The unique demands of aviation and aerospace applications often make anodizing the preferred option.

How to Choose Between Powder Coating and Anodizing?
A thoughtful evaluation of multiple factors becomes crucial when deciding whether to opt for powder coating or anodizing for aluminium finishing. In this intricate selection process, aesthetics, environment, and function are pivotal considerations.
Aesthetics
One must assess the desired visual appeal of the finished product. A powder coat can have various colours and textures, catering to diverse design preferences.
On the other hand, anodizing’s colour options, though limited, provide a more lasting and integrated appearance. The choice hinges on balancing immediate visual impact and long-term colour retention.
Environment
The surrounding environment significantly impacts the durability and longevity of the chosen finish. Suppose the aluminium parts are expected to endure corrosive atmospheres or extreme weather conditions. In that case, anodizing’s inherent corrosion resistance offers a distinct advantage.
Powder coating’s robustness remains undeniable, yet its vulnerability to chipping might necessitate an extra layer of protection in harsh environments.
Function
The function of the aluminium component must dictate the choice of finish. If the part is exposed to mechanical stresses or potential abrasion, powder coating’s scratch-resistant nature could be instrumental.
Meanwhile, if corrosion prevention is paramount, anodizing’s integrated oxide layer becomes indispensable.
Expert Opinion
In this intricate decision-making process, the role of experts cannot be overstated. Engaging with professionals who possess comprehensive knowledge of both finishing methods is essential.
These experts can evaluate the unique demands of each project, ensuring that the selected finish aligns optimally with its intended application.
Conclusion
The choice between powder coating and anodizing in aluminium finishes transcends mere aesthetics. It’s a decision that directly impacts durability, corrosion resistance, and overall functionality.
As we’ve navigated the intricacies of these processes, the significance of informed decision-making has become clear. Powder coatings and anodizing present distinct advantages, each catering to specific requirements.
Powder coating offers a broad spectrum of colours and robust protection against scratching, making it a strong contender. On the other hand, anodizing embeds corrosion resistance into the very structure of the aluminium, ensuring a longer lifespan.
In the dynamic landscape of surface treatment, Xometry emerges as a versatile and reliable service provider, offering powder coating and anodizing solutions. With a commitment to precision and excellence, Xometry caters to a diverse range of industries, fulfilling the nuanced requirements of each project.
Want some anodized or powder coated products? Pick your type and colour while uploading your model to our Instant Quoting Engine!
 Europe
Europe  Türkiye
Türkiye  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Global
Global 

 Login with my Xometry account
Login with my Xometry account  2
2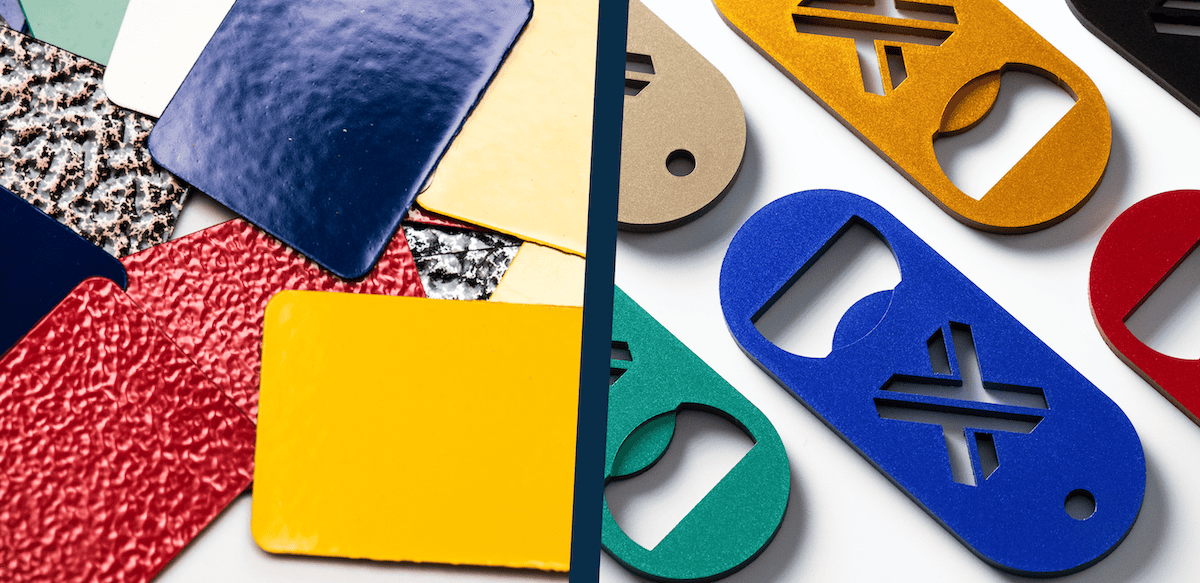








Comment(2)