In this blog, we answered the question, “How did the plastics that entered our lives in the last century affect our environment, our production, and consumption patterns, and where are plastic materials used today? How much more will these areas expand during the coming century?”
Use of Plastic Materials
The word plastic is derived from the Greek words “plastikos” and “plastos”, which mean shapeable or moldable. Most plastics are made by exposing fossil fuels, including natural gas, coal, or crude oil, to various chemical and physical reactions. Up until that point, the majority of the materials used in the manufacturing industries were made of metal, copper, or wood. Due to its heavy, low mobility, and energy-consuming inefficient structure, the use of metal has resulted in the emergence of expensive and unsustainable products. The use of wood and metal materials in production brought serious design constraints.
Formable plastics allowed manufacturers, design engineers and production teams in large industries such as transportation, packaging, white goods, construction to use manufacturing technologies that can give freedom, advanced performance and cost-effectiveness in innovative designs at the same time. And this allowed industries such as automotive and white goods to make mass production for general use.
Manufacturing is now much more flexible and fast as a result of expanding usage of plastic materials. Plastic materials that can be molded even at high temperatures, by melting, molding or processing, resulted in environmental performance improvements and cost savings in production. Today, a wide range of products, from t-shirts to eyeglasses, television screens to insulating gaskets, smartphones to microchips, are made from plastic materials.
Plastics are divided into thermoplastics and thermoset plastics according to their processing properties. The most important difference between thermoplastics and thermoset plastics is that, despite going through many cycles of melting and solidification, thermoplastics, which are the most common type of plastic, deform very little and are recyclable. High-performance polymers like PS, ABS, PC, and PP are the most commonly used thermoplastics. Thermoset plastics, on the other hand, cannot be remelted after being molded. Thermoset plastics solidify permanently after heating and cooling. Epoxy, resin and rubber are examples of thermoset plastics.

Choosing the Right Materials
In many industries, from consumer goods to medical equipment, pet bottles to cooking utensils, plastics are widely used to develop semi- or finished products. PVC is used in the production of glasses and carboys, PET is used in the production of pet bottles, while PC is used in the production of television screens and sunglasses. Rubber, parquet floors, and playground sponges are all made of polyurethane. And the majority of products made with PP material include phones, computer cases, hair dryers, and headphones.
The choice of material varies and has higher impact depending on where it will be used since it affects decisions made during the design, engineering, and manufacturing phases. Plastics like PP, ABS, and PLA are the most commonly used materials. High-performance plastics such as PEEK and Ultem, which can withstand deformations that may occur in long-term use of the produced tools for different production needs, are widely used in many sectors today.
Xometry Turkey offers a wide range of plastic material types and various manufacturing technologies. It is now much easier to select the most suitable one among thousands of plastics options, each with unique properties. If you think you need support regarding selecting the right material for your product, you can contact our expert team or you can get instant, accurate quotations that vary according to the material type on xometry.com.tr.
Sustainability and Recyclability
After the industrial revolution, new technologies have been developed quickly, making it simple to establish production facilities anywhere in the world. This uncontrolled growth and uncontrolled production process led to a serious increase in the number of waste materials. In the last 70 years, 8 billion tons of plastic have been produced, but 79% of that material is still in landfills and the environment today.
The ongoing demand for eco-friendly plastics in consumer products has driven all plastics-producing companies to pursue efficiency in all aspects of business while adhering to sustainable and environmentally friendly principles. In order to minimize the impact on natural resources, reduce waste production, and prevent the catastrophes like the climate crisis, it is vital for the future to develop sustainable manufacturing systems.
Plastic materials provide a number of advantages, including being lightweight and affordable, producing less waste, and improving environmental efficiency significantly. The environmental benefit can be improved by employing plastic materials that are measured with integrity and transparency in accordance with sustainable material management statistics.
Impact of Plastics on the Future
While the functionality of industrial 3D printing and plastic molding technologies has developed at a rapid pace, thousands of production sites have emerged in the last century where high-performance plastics are preferred over metal materials. The plastic material ratio used to be roughly 20–25% for products like refrigerators and televisions, today this figure has increased to 40-50%. Device applications with the best mechanical and chemical resistance properties have accelerated thanks to the newest plastic technologies. These engineering or general function plastics have enabled the manufacture of generally light, affordable, and complex geometries.
If you are a designer or engineer working on the product development process, you must stay up to date with the latest cutting-edge technologies available today and where manufacturing is headed in the future, but you also shouldn’t ignore the problems that the world we live in is currently facing. Companies that use plastic manufacturing technologies like additive manufacturing, machining, molding, and casting today aim to increase production efficiency and create environmentally friendly products by planning the process from early prototyping to final product design.
From smartphones to watches, from cars to food packaging, plastic materials are used in a wide range of industries. Attempts to build space stations and laboratory equipment entirely out of plastic materials demonstrate how plastic will effect our lives in the future. The development of plastic materials will continue to attract investment from manufacturers who aim to produce the most durable products at the lowest cost. It would not be incorrect to believe that we have reached the era of higher performance materials, with the need for plastic manufacture and R&D studies expanding significantly every day.
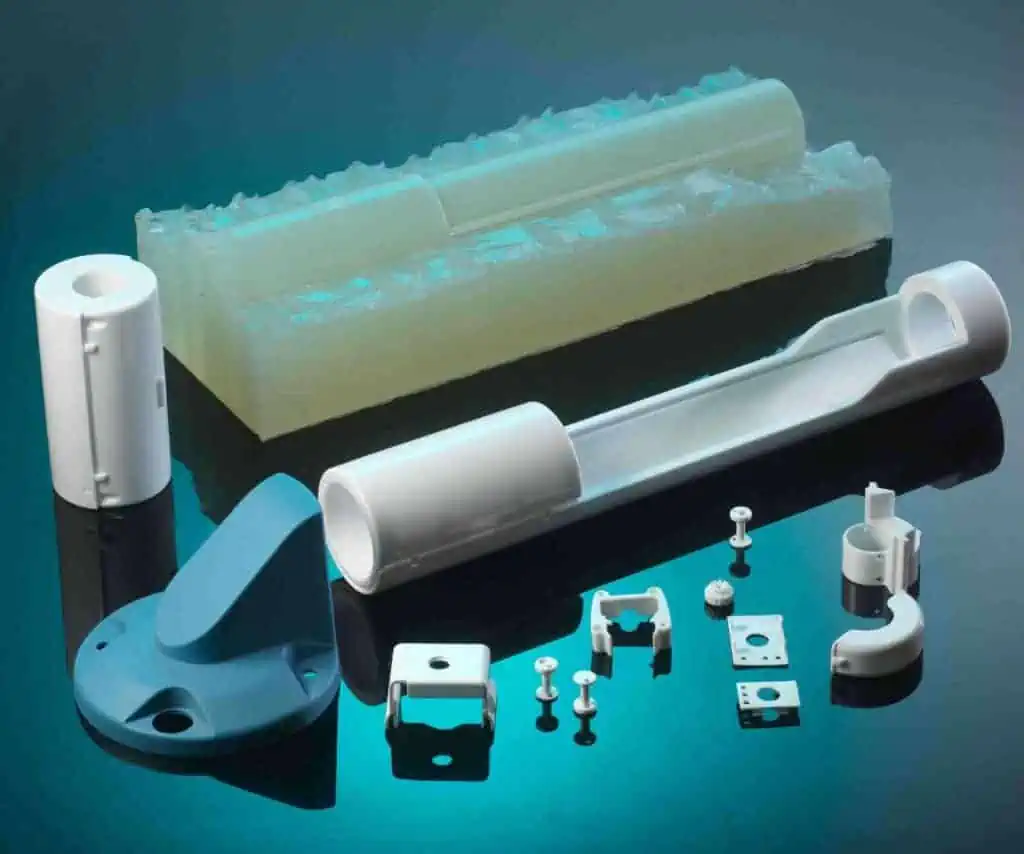

Highly Versatile Engineering Plastics
Plastic materials are used today to manufacture household appliances, durable consumer products, automobiles, spare parts, electronic devices and accessories, aerospace applications, and many more products.
Manufacturers have been able to develop products that are long-lasting, economical, and consumer-friendly thanks to the development of various rigid, flexible, transparent, and lightweight plastics with increased performance. Products with complex geometries have started to emerge as a result of plastics’ diverse qualities like high temperature and wear resistance, low maintenance costs, and energy efficiency. And thus it has created time efficiency and comfort for manufacturers and customers. Some of these versatile plastics include:
- PVC
- PC
- ABS
- HDPE
- TPU
- PETG
- PPO
- EHMW
- TPO
- LDPE
- Ultem
- PEEK
Turkey is the sixth in the world and the second in Europe among the plastic manufacturer countries. In an environment where there are so many production, manufacturers have developed different expertise in various plastic materials.
Xometry digitizes Turkey’s manufacturing and supply capability, identifies the expertise and services of certified manufacturers in the most precise way possible, and opens up the possibilities of seamless production to companies and individual clients who require assistance with manufacturing technologies. We leverage Turkey’s manufacturing power to provide you with the best manufacturing supply service possible, including transparency in procurement and manufacturing processes, sustainable energy strategies that reduce water and energy consumption, hundreds of material types, manufacturing supervision, and a wide range of material diversity.
Review the Services and Materials sections of xometry.com.tr to learn more about plastic manufacturing technologies and plastic materials.
 Europe
Europe  Türkiye
Türkiye  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Global
Global 

 Login with my Xometry account
Login with my Xometry account  0
0








Comment(0)