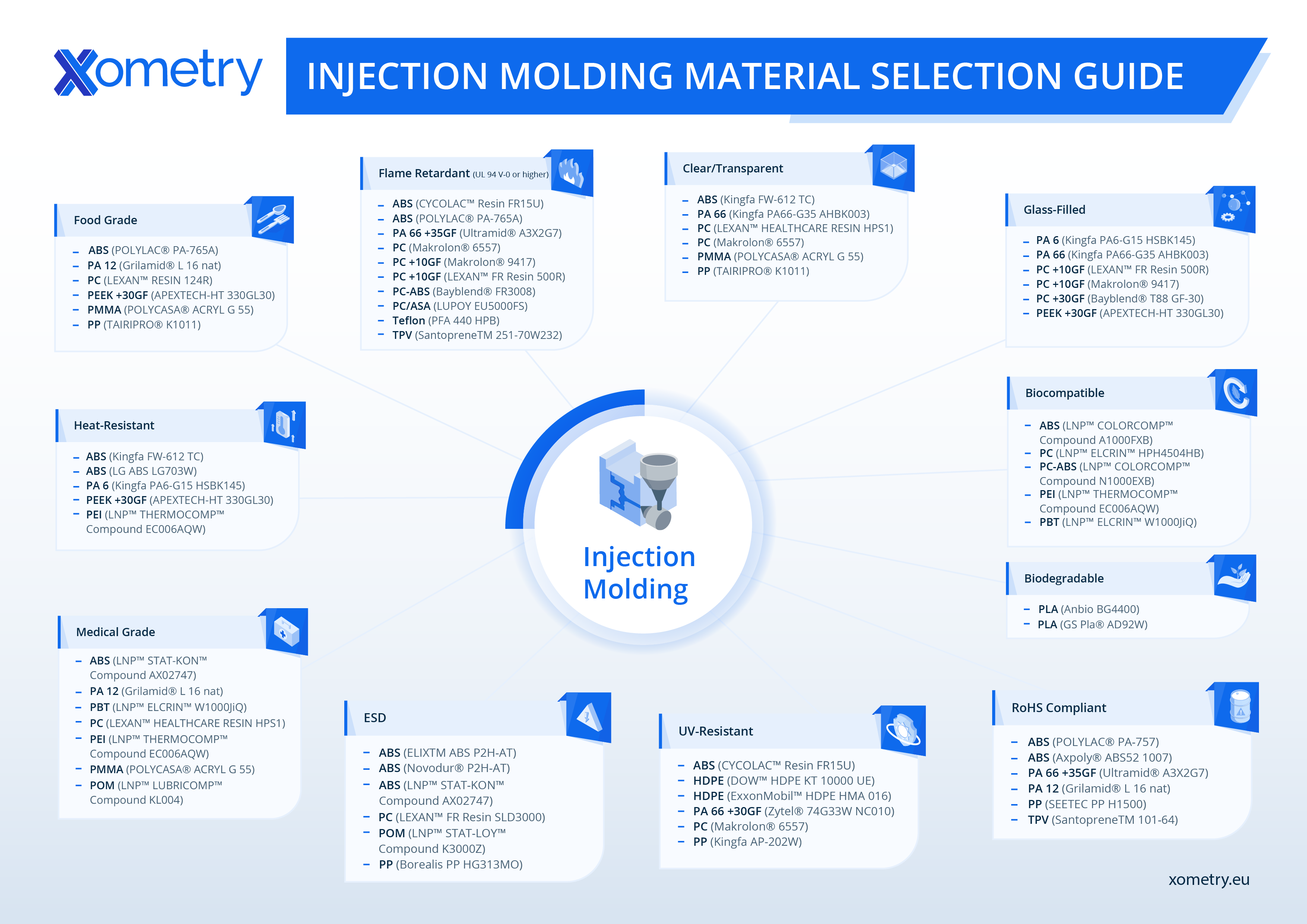
Material selection is an integral part of the injection molding process. It impacts the performance, cost and production time of a project. With such an important decision to make, choosing the right material can be daunting.
To make it easier for you, Xometry has put together a list of injection molding materials and their properties to help you select the best one.
Rigid Plastics
ABS
ABS is a widely used thermoplastic material. It is ideal for producing parts with good impact resistance, low cost and high tensile strength. It offers high surface hardness, chemical resistance and toughness. Good heat resistance also makes it ideal for producing parts with a glossy finish, which is often desired in the automotive industry. It gives a high resistance to scratch for outdoor applications. All these features make ABS a very popular choice for injection molding.
- Key features: High rigidity • Resistance to scratches • Good strength-to-weight ratio • High weldability
- Applications: ABS is widely used in the manufacture of automotive and marine parts
- See the datasheet
Acrylic (PMMA)
Acrylic (PMMA) is commonly used when optical clarity is a necessity. This thermoplastic offers excellent optical transparency even at very thin wall thicknesses, making it ideal for applications like lenses and face shields. It is a great substitution for glass for outdoor use. Acrylic shows high moldability which can be used to form various different shapes and sizes in injection molding.
- Key features: Good abrasion resistance, impact strength and weatherability properties
- Applications: It is used in the manufacture of windows, frames, mobile screens etc.
- See the datasheet
HDPE
HDPE provides excellent impact resistance and chemical resistance. It is an ideal choice for producing parts with excellent toughness and rigidity. HDPE offers high heat resistance and a low coefficient of expansion. Its good temperature stability makes it ideal for applications where parts must retain their shape under extreme temperature changes. It also provides good electrical insulation.
- Key features: HDPE is a lightweight, chemical resistant and environmentally friendly material
- Applications: It is best used for heavy construction, agriculture and the manufacture of medical products
- See the datasheet
LDPE
LDPE is a resilient thermoplastic, making it an ideal choice for applications requiring good impact resistance. It also has excellent chemical resistance properties, as well as a melting temperature of 115°C. Its flexibility makes it suitable for intricate shapes requiring high levels of detail and dimensional accuracy. Its low cost also makes it a great choice for the mass production of injection moulded parts.
- Key features: Lightweight • Translucent • Resistant to stress
- Applications: LDPE is commonly used in food containers, toys, and industrial and medical parts
- See the datasheet
Nylon 6 / PA 6
Nylon 6 is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic that offers excellent wear resistance, chemical resistance, and toughness. It can be used in combination with other materials to enhance its properties further. The fibre in the material is tough but gives good elasticity to the product. Nylon 6 is also suitable for applications requiring tight tolerances. It also gives good resistance to wear with good electrical
- Key features: Rigid • High strength • Resistant to wear and chemicals
- Applications: It is best suited for bearing, gears, and electronic connectors
- See the datasheet
Nylon 66 / Nylon 6/6
Nylon 66 is a synthetic polyamide that offers excellent strength and toughness, making it suitable for applications with high-impact requirements. It has a high melting temperature of 258°C and a good tensile strength of 85 MPa. However, it shows no resistance against UV rays. With its good sliding property, Nylon 66 makes an excellent choice for many injection molding applications.
- Key features: Light weighted • Good mechanical strength • Stiff • Wear resistance
- Applications: Nylon 66 / Nylon 6/6 are commonly used in making brushes, tennis strings, surgical sutures
- See the datasheet
PBT
PBT is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic that offers excellent mechanical strength, rigidity, and heat resistance. It has a high melting point of 215°C which makes it a good choice for injection moldings. PBT shows good chemical resistance. It also offers good dimensional stability and tight tolerances, as it has a low coefficient of expansion. Its good temperature resistance makes it suitable for applications that require parts to maintain their shape under extreme temperature changes.
- Key features: Abrasion resistant • Good dimensional stability • Low coefficient of thermal expansion
- Applications: PBT is mostly used in gears, bearings and iron handles, motor brackets
- See the datasheet
PC (Polycarbonate)
PC is a transparent thermoplastic with excellent impact resistance, shatter resistance and stiffness. It also has good chemical resistance properties. PC’s transparency makes it ideal for applications where visibility of the internal parts is required. Its high melting point of 250°C makes it suitable for various engineering processes. It shows high stiffness and high viscosity which makes it suitable for parts requiring high dimensional accuracy and tight tolerances.
- Key features: Shatter resistance • Good electrical properties • Transparent • Durable
- Applications: It is widely used in medical devices, eyewear, electronics and beverage packaging
- See the datasheet
PS-ABS Polycarbonate
PS-ABS Polycarbonate Blends are a special type of injection molding material that combines the strength, heat resistance and rigidity of a PC with the flexibility and cost savings of ABS. It is ideal for parts requiring high-temperature stability, good chemical resistance and dimensional accuracy. PS-ABS also offers excellent impact resistance, making it suitable for applications requiring parts that are durable and perform well under shock and vibration.
- Key features: High impact strength • Heat resistance • Flexibility
- Applications: PS-ABS is suitable to produce parts like keypads, panels, TV frames etc. for the electronics industry
- See the datasheet
PC-PBT
PC-PBT is a special thermoplastic which combines the high mechanical strength, heat resistance and rigidity of a PBT with the shatter resistance and stiffness of a PC. It is widely used in the manufacture of automotive and aerospace parts as it offers a high strength-to-weight ratio and good chemical resistance. It is also used for parts that require high corrosion resistance.
- Key features: Heat and corrosion resistance • Dimensionally good mechanical strength
- Applications: This material is mostly used in the manufacture of automotive bumpers and gear cases
- See the datasheet
PEEK
PEEK is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic offering excellent mechanical strength and stiffness, as well as high temperature resistance. It has a low thermal coefficient of expansion, making it suitable for precision parts with tight tolerances. Its chemical resistance and wear resistance is also very good. PEEK can be used in combination with other materials to enhance its properties further. It shows high resistance to stress cracking and has excellent dimensional stability. Best used for parts where shock and vibration are a concern.
- Key features: Chemical and fatigue resistance • High mechanical strength • High chemical resistance
- Applications: PEEK is commonly used for medical implants, electric insulations, seals and valves
- See the datasheet
PEI (Ultem)
PEI (Ultem) is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic offering excellent mechanical strength and stiffness, as well as high temperature resistance. It is one of the most popular materials used in injection molding thanks to its excellent electrical properties. It is also widely used for its exceptional dimensional stability. It boasts superior flame retardant properties and can be used in a variety of applications, from automotive and electronics components to medical equipment and machinery.
- Key features: Heat resistance • High dielectric strength • Good stiffness and hardness
- Applications: It is used in engine components, temperature sensors, medical devices etc.
- See the datasheet
PET
PET is another common material used in injection molding. It has excellent mechanical and thermal properties, making it ideal for parts that need to be lightweight and shatter-resistant. PET also has outstanding chemical resistance, so it can withstand exposure to many chemicals without degrading or becoming brittle. Additionally, it has good aesthetic properties – it has a glossy finish and is easy to dye, allowing for parts with vivid colours. Its high melting point requires the molding to be done at a high temperature.
- Key features: Flame retardant • Heat, creep and chemical resistant
- Applications: PET is used in the making of capacitors, bottles, recording tapes and many other electrical components
- See the datasheet
PLA
PLA is a bioplastic derived from renewable sources such as cornstarch and sugarcane. It has excellent mechanical properties, making it a great choice for parts that require strength and flexibility. PLA also has good thermal stability, allowing it to remain strong at high temperatures. It has a low melting point of 145 – 160°C. PLA is recyclable and biodegradable, making it a great choice for environmentally friendly manufacturing.
- Key features: Biocompatible • High tensile strength • Low glass transition temperature • High flexibility
- Applications: PLA is commonly used in plastic films, bottles and medical devices
- See the datasheet
Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene (PE) is a lightweight but tough material that can withstand high impact and has excellent chemical resistance. It is the most widely used plastic in the world. It is derived from petroleum and shows a good strength-to-weight ratio. It also offers dimensional stability – its parts will retain their shape even when exposed to extreme temperatures or pressure. Polyethylene is also recyclable, making it a great option for many applications.
- Key features: Impermeable • Chemical resistant • Exhibits good electrical insulation properties
- Applications: This material is commonly used in garbage and grocery bags, packaging films, bottles and food packaging containers
- See the datasheet
Polypropylene (PP)
PP is a widely used thermoplastic with high strength and excellent elasticity. It can be clear or coloured and is widely used in the manufacture of car parts, electrical components and packaging materials. It has good moisture resistance, making it suitable for use in high-temperature applications, and can be formed into various sizes and shapes through injection molding. It is also resistant to heat, fatigue and electrical insulation.
- Key features: Heat, chemical and moisture resistant • Good elasticity • High impact strength
- Applications: PP is used in making carpets, clothing and camping equipment for domestic use. Car batteries, bumper and cladding for industrial use
- See the datasheet
Polystyrene (PS)
PS is a transparent amorphous thermoplastic made from monomer styrene. It is a hard material with high strength, making it suitable for use in a variety of applications. It shows good electrical properties and is resistant to gamma radiation. It can be formed into various sizes and shapes through injection molding, making it a popular choice for household items and other plastic products.
- Key features: Transparent • Hard and brittle • Excellent strength
- Applications: PS is widely used in the making of disposable cutlery, food containers, plates, bowls etc.
- See the datasheet
POM / Delrin acetal
POM, also known as Delrin Acetal, is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic with excellent strength and wear resistance. It can be easily formed into different shapes through molding processes and has good chemical resistance properties. POM is often used in industrial applications because of its high tensile strength of 75.8 MPa. It is mostly tough and durable with low moisture absorption properties.
- Key features: Wear resistant • Strong and durable • High tensile strength
- Applications: This material is generally used in the manufacture of mechanical parts such as pumps, valves and bearings etc.
- See the datasheet
PPE-PS
PPE-PS blend is a combination of PPE and PS. It offers superior mechanical properties. This allows for improved impact strength and stiffness. It can also be used in applications requiring high temperature resistance as well as electrical insulation. It gives a good surface appearance and is highly ductile. PPE-PS shows a good tensile strength of 50 MPa at room temperature.
- Key features: Ductile • Strong • Good flow ability • Impact resistant
- Applications: PPE-PS is best used in making valve components, water pumps and various medical devices
- See the datasheet
PPS
PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide) is a semi-crystalline thermoplastic with good chemical resistance, high heat deflection and UV light. It has exceptional dimensional stability and can be used in applications requiring good electrical insulation. PPS is highly fire resistant. It has a good tensile strength of up to 80 MPa at room temperature which makes it a popular choice for automotive parts.
- Key features: Rigid • UV and chemical resistant • Good dimensional stability
- Applications: PPS is mostly used in fuel injection systems, switches, and electronic devices like steam iron and hair dryers
- See the datasheet
PSU
PSU (Polysulfone) is a semi-crystalline known for its high-temperature stability. It has excellent electrical insulation, dimensional stability and very good chemical resistance. PSU also offers improved impact strength over other plastics. Its tensile strength can reach up to 80 MPa. PSU is ideal for applications requiring excellent mechanical properties and heat resistance such as automotive parts, electrical components and medical devices.
- Key features: Thermal stability • Strong and durable • Chemical and heat resistant
- Applications: PSU is mostly used in the automotive, medical and electrical industries, such as electrical insulators and applications
- See the datasheet
Injection Molding Rigid Materials Comparison Table
| Rigid material | Tensile strength (MPa) | Elongation at break (%) | Hardness (Shore D) |
| ABS | 46 | 48 | 68 – 118 |
| Acrylic (PMMA) | 55.1 – 75.8 | 2 | 98 |
| HDPE | 25 | 9 | 64 |
| LDPE | 9.6 | 100 | 55 |
| Nylon 6 / PA 6 | 40 | 60 | 81 |
| Nylon 66 / Nylon 6/6 | 85 | 70 | 168 |
| PBT | 130 | 2.5 | 170 |
| PC (Polycarbonate) | 65.5 | 60 | 95 |
| PS-ABS Polycarbonate | 41 | 6 | – |
| PC-PBT | 41.8 | 4.6 | 109 |
| PEEK | 99.9 | 35 | 230 |
| PEI (Ultem) | 113.7 | 80 | 165 |
| PET | 91 | 15 | 195 |
| PLA | 49.5 | 5.2 | 83 |
| Polyethylene (PE) | 21 | 11 | 64 |
| Polypropylene (PP) | 30 | 150 | 70 |
| Polystyrene (PS) | 16 | 35 | 80 |
| POM / Delrin acetal | 75.8 | 30 | 150 |
| PPE-PS | 50 | 30 | 89 |
| PPS | 93 | 15 | 95 |
| PSU | 80 | 50 | 93 |
Elastomers and Synthetic Rubbers
PVC
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is a thermoplastic produced from vinyl chloride. It has excellent chemical resistance, good machinability and flexural strength making it suitable for use in a wide range of applications. PVC is also UV resistant and can be easily formed, cut or shaped into different sizes and shapes through injection molding. It is the third most synthesised thermoplastic with light weight and good insulation properties. It is widely used in the construction industry and for medical applications.
- Key features: Weather resistant • Chemical, corrosion and shock resistant • Biocompatible and high strength
- Applications: It is mainly used for manufacturing pipes, windows frames, bottles, electrical distribution boxes etc.
- See the datasheet
TPE (Elastomer)
TPE (Elastomer) is a special type of injection molding material that combines the versatility of rubber with the strength and heat resistance of thermoplastics. It is often used in place of traditional rubber and plastic materials as it is more flexible and durable. It offers excellent temperature resistance and good chemical resistance. TPE also offers good wear resistance making it a popular choice for automotive parts and gaskets. It is available in various grades and designed for specific applications.
- Key features: Flexible • Strong • Durable • Tear and abrasion resistant
- Applications: TPE is commonly used in grips, handles, seals, power and hand tool components, wires and cables
- See the datasheet
TPV (rubber)
TPV (thermoplastic vulcanizates) is a special type of synthetic rubber produced through a combination of thermoplastics and elastomers. It has good chemical resistance, flexibility, and high tensile strength. TPV can also be used in applications requiring low-temperature performance and superior impact resistance making it a great option for outdoor use. It is widely used in automotive and industrial applications requiring a combination of rubber-like properties and heat resistance. These materials are also lightweight and easy to process.
- Key features: High strength • UV and heat resistance • Durable • Flexible
- Applications: TPV is widely used on the market including tires, hoses and gaskets
- See the datasheet
Injection Molding Elastomers and Synthetic Rubbers Comparison Table
Source Your Custom Injection Molded Parts at Xometry
Choosing the best material for your next injection molding project can be a very complex task. At Xometry, we have a wide range of materials that are suitable for your projects and can help you find the perfect one to suit your needs. Our material selection offers the best combination of strength, flexibility, and heat resistance to suit your application.
Upload your files to Xometry’s Instant Quoting Engine to get a quote within 48 hours.
 Europe
Europe  Türkiye
Türkiye  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Global
Global 

 Login with my Xometry account
Login with my Xometry account  0
0









Comment(0)