Injection molding is a plastics manufacturing technology that is capable of very high production volumes. The process works by injecting liquid plastic into a mold at very high pressure. Compression molding, on the other hand, is better suited to medium-volume production and is typically used with rubbers and silicones.
Injection molding is better suited to creating complex parts, whereas compression molding is better suited to simple geometries and large panels. Injection molding is highly automated and does not need constant human supervision, while compression molding often requires human intervention to load a charge and remove completed products. Tooling is also cheaper for compression molding.
Injection Molding Definition and Comparison to Compression Molding
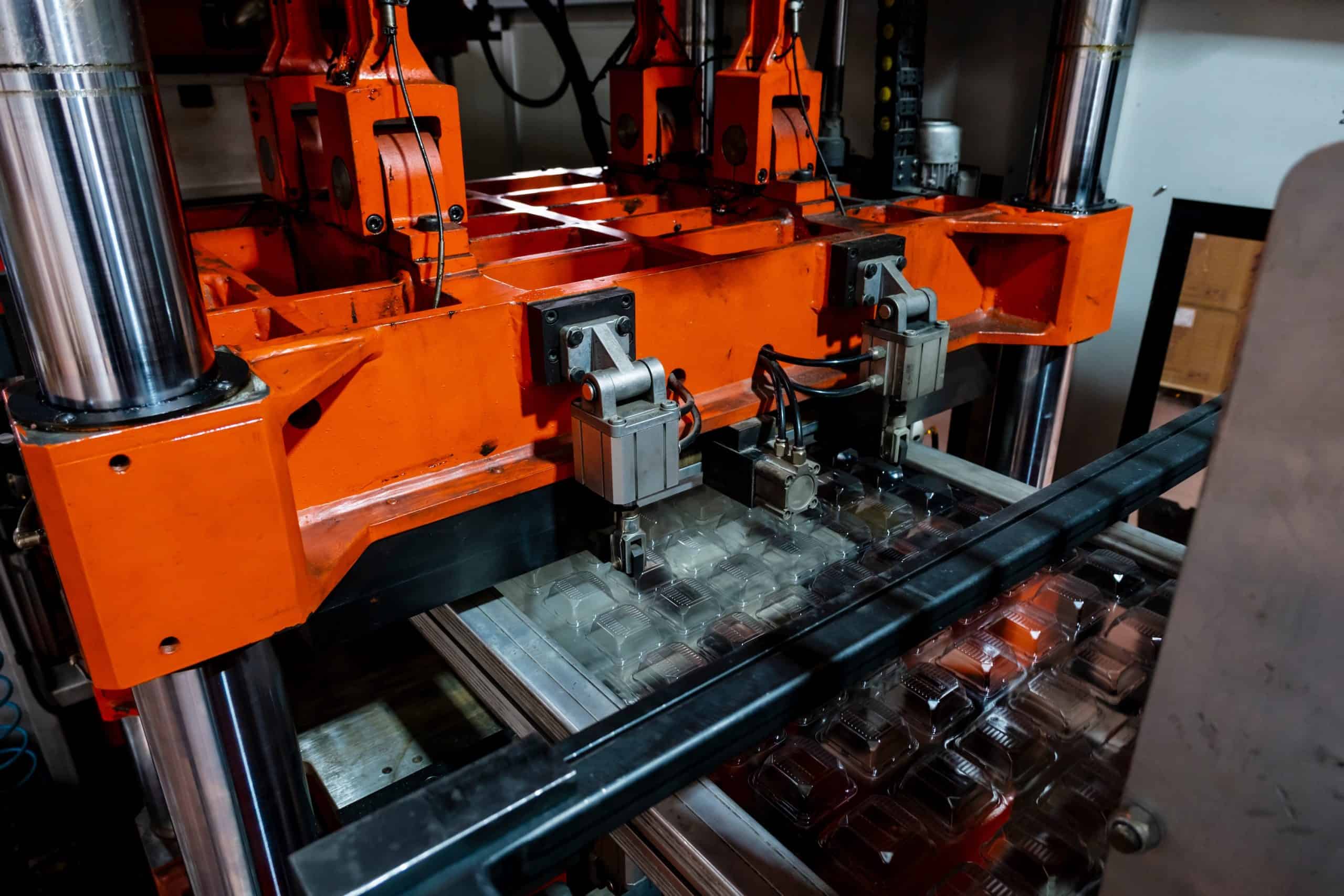
Injection molding works by injecting molten thermoplastic into a mold cavity. During the plastic injection process, the plastic resin pellets are melting inside a barrel. The barrel contains a screw with a shaft whose diameter increases along its length. As the screw rotates, plastic is forced into an incrementally smaller volume. This compression is the primary mechanism responsible for melting the plastic. The barrel is also heated to supply additional heat. Once enough plastic to fill the mold has melted, the screw retracts and then is pushed forward to force the plastic resins into the mold at very high pressures.
Molds are made from at least two components and are held together with hydraulic rams so that the high-pressure plastic injected into the mold cannot escape from the parting line. The mold has cooling channels that cool the part enough so that it can be ejected from the mold without damaging it. Injection molding can achieve high production volumes unmatched by any other plastic processing technique. Compression molding, on the other hand, is better suited to medium-volume production.
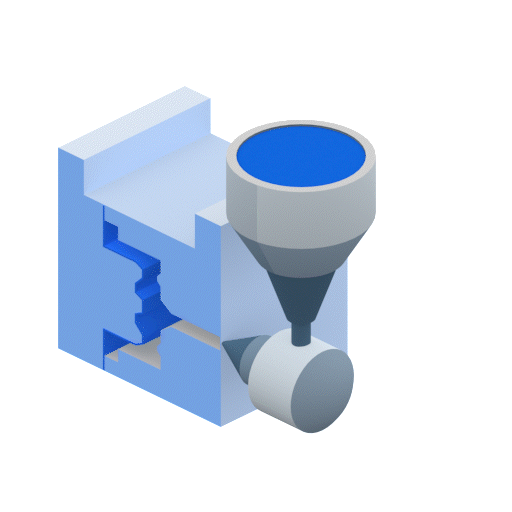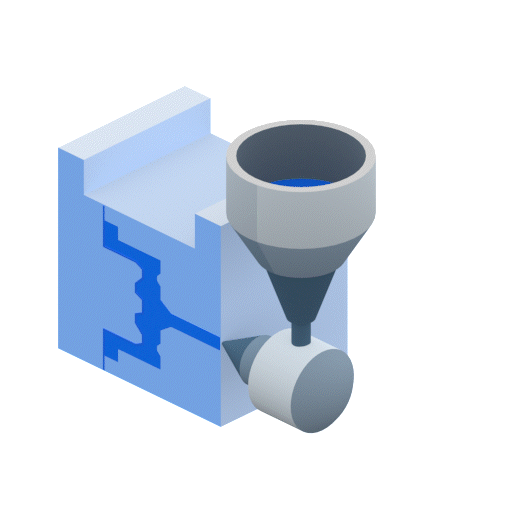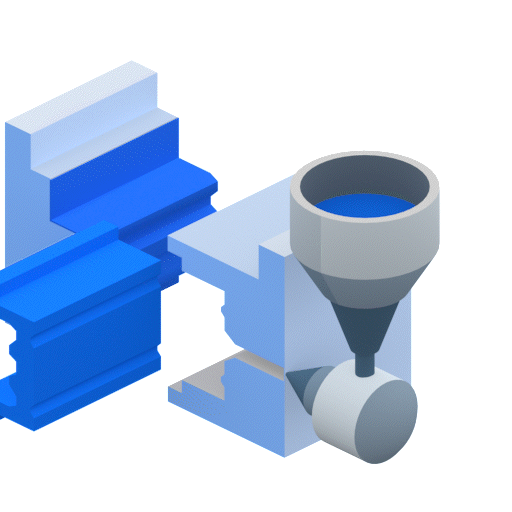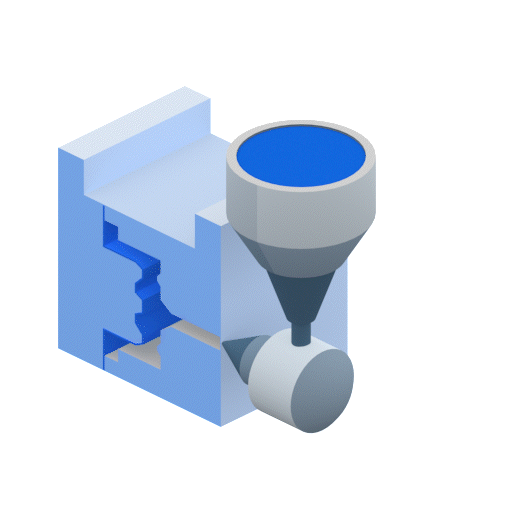
Advantages of Injection Molding Compared to Compression Molding
Listed below are some advantages and disadvantages of injection molding compared with compression molding:
- Injection molding is a method for large production runs that can produce millions of parts per machine annually.
- Due to the high levels of automation and rapid manufacturing speed, injection molded parts are cheaper than compression molded parts.
Disadvantages of Injection Molding Compared to Compression Molding
Listed below are some disadvantages of injection molding compared with compression molding:
- Injection molding requires very high plastic injection pressures. The mold must therefore be built to withstand these high pressures. This adds cost to the tooling.
- Injection molding is not well suited to manufacture large, thin parts like vehicle panels.

Compression Molding Definition and Comparison to Injection Molding
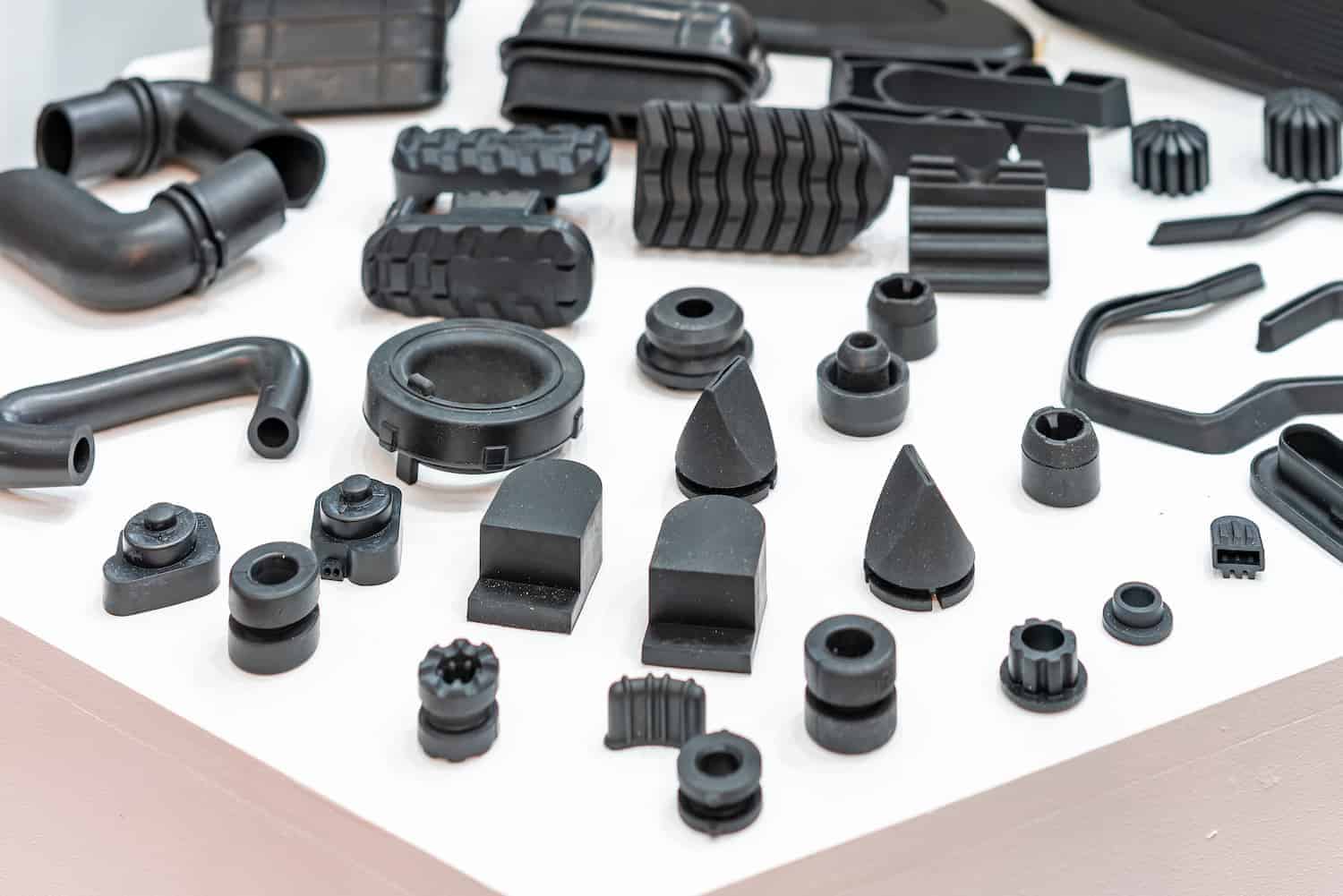
Compression molding is a process most often used to manufacture parts from pliable materials. This molding technique typically employs a two-part mold, with one part fixed to the base of the compression molding tool while the top half is free to move up and down. The molds are usually heated to help cure the final product while also heating the charge before compression. A precisely weighed-out charge is heated until it is pliable. It is then placed into the bottom half of the mold.
The top half then moves down and forces the charge to conform to the desired shape of the mold. The heated mold stays closed while the material is allowed to cure. This typically takes a few minutes. Once cured, the part is removed from the mold. Post-processing is required to cut off any flash. Flash (or excess material at the parting line of the mold) is a common occurrence for compression-molded parts.
Compression molding is used for creating reinforced panels. The process involves laying out fibre-filled plastic sheets in the bottom half of the mold. Thereafter, the top half of the mold compresses and heats the material to force the plastic throughout the mold, creating a composite part. This is how large plastic car bumpers are made.

Advantages of Compression Molding Compared to Injection Molding?
Listed below are some advantages of compression molding compared to injection molding:
- Compression molding can make use of SMC (Sheet Molding Compound) and BMC (Bulk Molding Compound) to create composite panels. These panels do not have continuous fibre-impregnated sheets, but rather chopped fibre strands that are distributed throughout the bulk material. The injection molding method cannot make composite material parts.
- Compression molds do not need to withstand high internal pressures as do injection molds. Instead, the only load they experience is a compression force from above. This means that compression molds tend to be less expensive.
Disadvantages of Compression Molding Compared to Injection Molding
Listed below are some disadvantages of compression molding compared to injection molding:
- Compression molding is a very manual and slow process. Even if a robot arm is used to add the charge and remove the product, the cycle time between parts is still much slower than injection molding due to the need for the parts to be set before being removed.
- Compression molding cannot create plastic parts with high levels of complexity. The materials used are typically very viscous and as a result, they don’t flow well into small, complicated features.

Comparison Table Between Injection Molding and Compression Molding
Attributes of compression molding and injection molding are shown in the table below:
| Attribute | Injection Molding | Compression Molding |
| High-volume production process | Yes | No |
| Materials | Thermosets, thermoplastics (including fibre and metal-filled), thermoplastic elastomers, metal-filled polymers, fibre-filled thermoplastics | Thermosets, thermoplastics, silicone, unvulcanized rubber, BMC, SMC |
| High tooling cost | Yes | No |
| Can produce large, thin-walled panels | No | Yes |
| Post-processing required | Yes | Yes |
Injection molding is better suited to high-volume production whereas compression molding is better suited to pliable and flexible materials. Compression molding also has cheaper tooling costs.

Injection Molding Vs. Compression Molding: Lead Cost Comparison
When it comes to individual part cost, injection molding can produce inexpensive, complex parts. However, this manufacturing process is only cost-competitive if production run volumes are large enough to spread the high cost of injection molding tooling over a sufficient number of pieces. At lower volumes, compression molding is cheaper than injection molding due to the lower initial mold costs.
Injection Molding Vs. Compression Molding: Speed Comparison
Injection molding is significantly faster than compression molding. The cycle time for injection molded parts can be a few seconds, whereas compression molding cycle times can easily reach a few minutes. This is because compression molded components often need to cure thanks to the heating process before they are removed from the mold.
Injection Molding Vs. Compression Molding: Volume Comparison
Injection molding is a high-volume production method that is unmatched by any other manufacturing technology. Injection molding processes can be fully automated, while compression molding often requires a person to place the raw materials into the mold, remove it, and post-process it.
Injection Molding Vs. Compression Molding: Materials Comparison
Injection molding can make use of rigid thermoplastics as well as thermoplastic elastomers. Compression molding more often makes use of flexible elastomers like rubber and silicone, but can also produce rigid composite components by making use of SMC and BMC.
Summary
This article presented the comparison of injection molding to compression molding, explained what they are, and discussed the different attributes of each.
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities, including plastic injection molding, compression molding and other value-added services for all of your prototyping and production needs.
 Europe
Europe  Türkiye
Türkiye  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Global
Global 

 Login with my Xometry account
Login with my Xometry account  0
0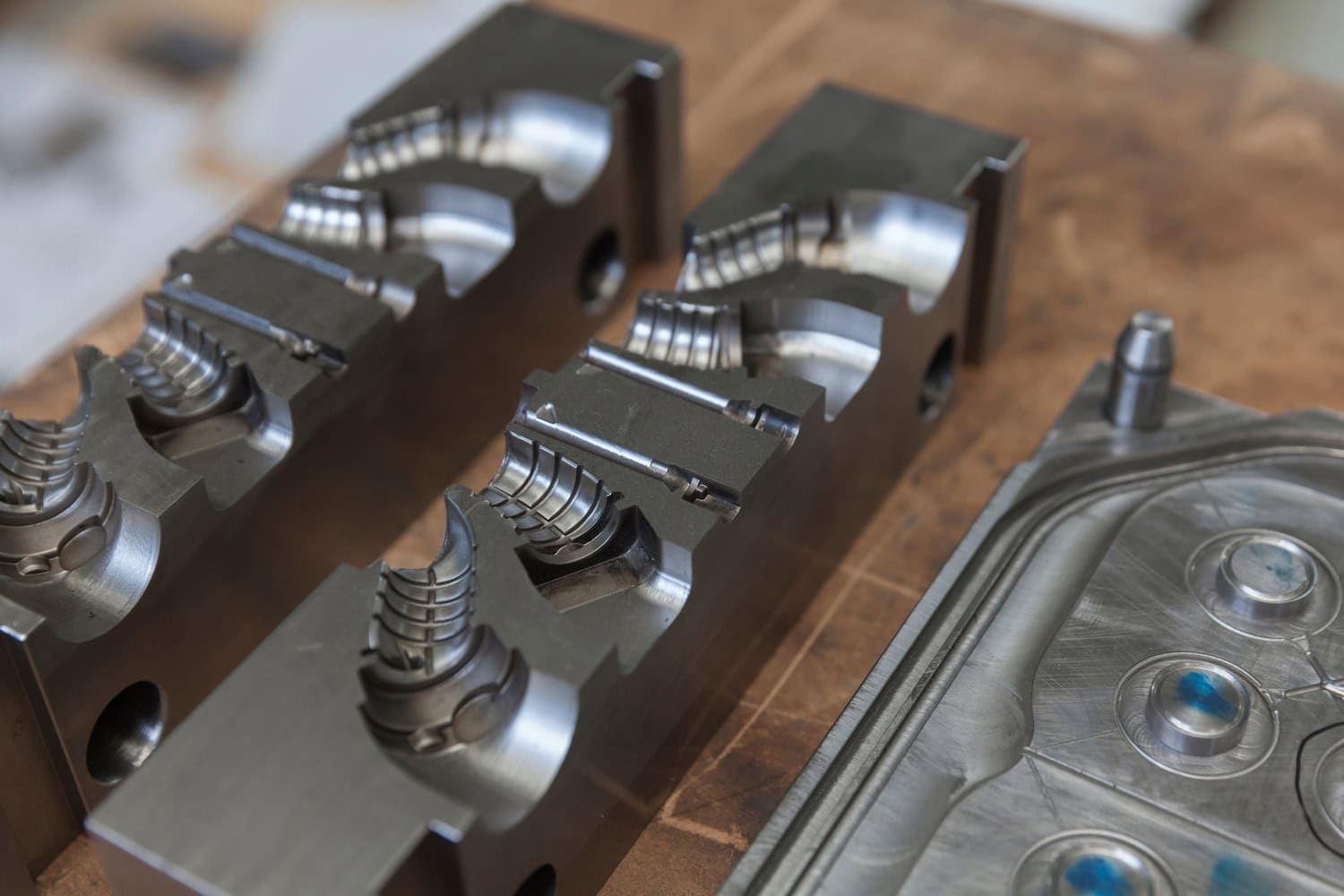








Comment(0)