Casting and injection molding are two common manufacturing processes that are used to fabricate many of the products we encounter every day. Polyurethane, a thermoplastic material, is commonly used to make parts such as gaskets in automotive settings, casters and rollers for medical carts, and various hardware such as pulleys, bushings, shock absorbers, and scraper blades
To determine whether vacuum casting vs. injection molding is better for your particular application, consider whether the part is for prototyping or mass production and identify how many parts you intend to create.
What is Vacuum Casting?
Vacuum casting is the process of creating parts by pouring liquid plastic into a mold under a vacuum. The mold is typically made from a soft material such as silicone. Molds filled with liquid plastic are then placed in an oven to cure. However, not all plastics require heating to cure. Some can cure at room temperature over time. Once cured, the mold is opened and the casted part can be removed.

The vacuum casting process is often used to create finished plastic parts for small production runs or for the rapid prototyping of a product that will eventually be injection molded.
The soft molds for vacuum casting are created from a “master pattern.” A master model is a 3D-printed or CNC-machined replica of the part to be cast. The master pattern is then dipped in liquid silicone which then cures and sets. Once set, the master pattern is cut in half and the 3D-printed or CNC-machined portion is removed. This process leaves behind two mold halves whose internal cavities, taken together, are identical to the part to be cast.
What is the Lead Time of Vacuum Casting for Production?
Lead times of production-level vacuum casting usually run from 1-2 weeks. While the master pattern and mold for vacuum casting can be completed between three to seven days, satisfying production volumes can take longer. This is because the plastic must cure before it can be removed from the mold, and curing time can’t be abbreviated.
The production output for a single vacuum casting mold is generally about 1-10 parts per day. The output largely depends on factors such as the type of plastic and part geometry.
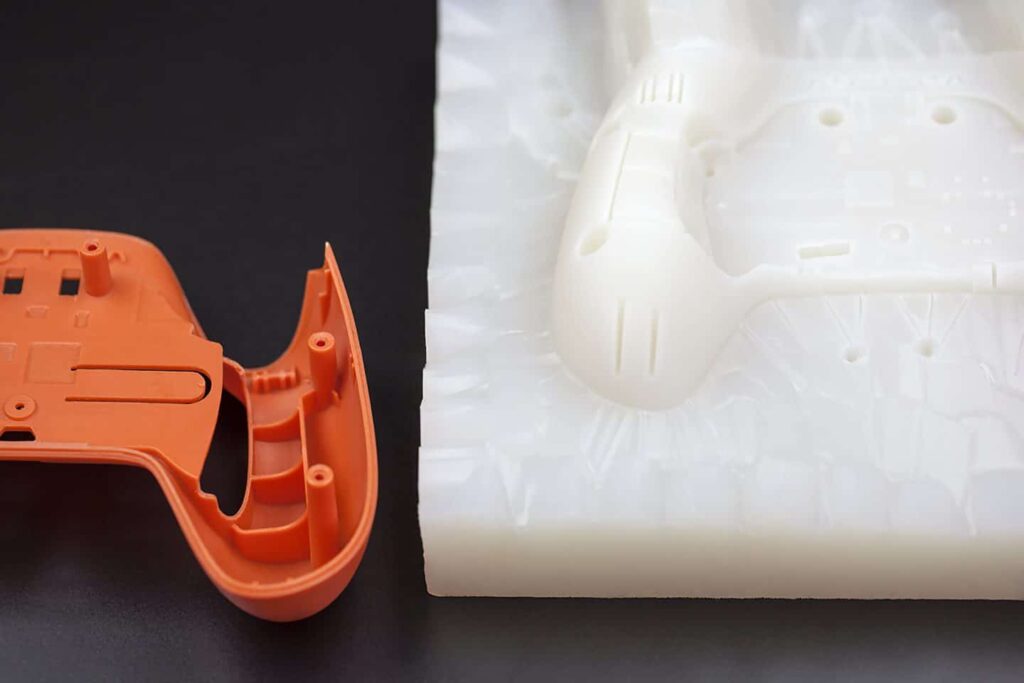

How is the Volume Produced by Vacuum Casting?
The volume of products produced by vacuum casting is small compared to other manufacturing methods. This is primarily because vacuum casting is a labour-intensive, manual process. It contrasts sharply with injection molding or CNC machining processes which are heavily automated and require little manual intervention. Casting plastics must be prepared properly before casting. Some plastics may be purchased already in their liquid state. Others are purchased solid and must be melted in an oven.
Once liquified, plastics must be mixed at the appropriate ratios with different chemicals to facilitate proper curing and to obtain desirable characteristics such as a particular colour. Additionally, these ratios can be adjusted to achieve properties such as abrasion resistance or increased compressive strength.
While some fast-setting plastics can cure within 30 minutes, others may take several hours to cure. All these aspects make the process suitable for prototyping and small-scale production runs, but not large manufacturing operations.
What Are the Tools and Parts Cost for Vacuum Casting?
The tools and parts required for vacuum casting are significantly cheaper than those associated with other manufacturing methods. Silicone for the molds is inexpensive and it’s much easier to create these flexible molds than to make die sets for injection molding.
Additionally, suitable plastic resins and curing agents are affordable. The main barrier tends to be the master pattern since SLA printers or CNC machines are very costly. Many manufacturers outsource their master-pattern production to third parties. This, in many cases, is still significantly more cost-effective than other manufacturing technologies like injection molding.
What is the Tolerance of Vacuum Casting?
Vacuum casting tolerances typically start around 0.3 mm, though they can vary depending on several factors. The type of plastic, part size, and part complexity can all influence the tolerance of a vacuum-cast part. Tolerances can vary on a case-by-case basis.
Is Vacuum Casting Expensive?
No, vacuum casting is not expensive. It is cost-effective for both prototyping and manufacturing (depending on the production volumes required).
What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is the process of forming highly precise products by forcing molten plastic material into the cavities of a mold at very high pressure. This is unlike the casting process where gravity helps the plastic resin fill out the mold cavity. In injection molding, the pressurised filling of cavities and rapid cooling of plastic parts makes it a significantly faster and repeatable process than casting. As such, it’s an ideal process for large-scale manufacturing operations.
Molds for plastic injection molding are fabricated through methods like CNC machining and electric discharge machining (EDM). These two processes can form cavities to tolerances as tight as ±0.1 mm on average and, in some cases, may get as low as ±0.025 mm depending on the application.
Because of the high pressures and temperatures involved, molds for injection molding are typically made from hardened steel or aluminium.
What is the Lead Time for Injection Molding for Production?
Lead times for the actual injection molding tooling are long. The precision necessary in the metal molds requires time to perfect. Once the molds are completed, however, injection molding production needs less lead time than casting. Large quantities of plastic parts can be completed at a much faster pace.
The high pressure and rapid cooling make for a much faster cycle time. While some die sets for injection molding have only one or two cavities, others may have well over 100. This means injection molding can produce hundreds, if not thousands, of parts per day to fulfil production orders.
How is the Volume Produced by Injection Molding?
The volume of parts possible through injection molding is significantly higher than that produced by casting. Injection molds can have multiple cavities for identical plastic components and overall cycle times are short.

What is the Tools and Parts Cost for Injection Molding?
The tools and parts required for injection molding are much costlier than those needed for vacuum casting. Die sets for injection molding are typically fabricated from metals such as hardened steel or aluminium and are made to precise tolerances. Several machining processes and post-processes are required to create a viable mold.
Die sets are typically composed of many different parts such as ejection pins, springs, and limit switches. The cost of manufacturing and assembling die sets for injection molding quickly runs into the thousands, or in some cases, hundreds of thousands of euros.
What is the Tolerance of Injection Molding?
Proper dimensions and tight tolerances in injection molding are the most important things with respect to design and manufacturing. This is why we recommend referring to the industry standards DIN 16742:2013 where general tolerances for different linear dimension ranges are presented.
How to Choose the Right Manufacturing Process
When deciding whether vacuum casting or injection molding is the right manufacturing technique, consider the items listed below:
- Production Volume: Vacuum casting is better for prototyping or small production runs, while injection molding is better for medium-to-large production runs. Casting can produce 1-10 parts per day while injection molding can produce hundreds, if not thousands, depending on the number of cavities in your mold.
- Tooling Cost: The tooling for vacuum casting is much cheaper than for injection molding. Plastic resin, curing agents, and silicone molds for casting are far less expensive than the hardened steel or aluminium die sets necessary for injection molding.
- Part Cost: Vacuum cast parts are more expensive than injection molded parts because of the manual labour and low volumes produced by casting.
- Material: Only a limited set of curable plastics can be used for casting while an extensive variety of thermoplastics and thermosets can be used with injection molding.
- Lifespan: Silicone molds for vacuum casting are not as durable as hardened steel or aluminium injection-ready molds that can last decades. Consider how long you expect to need your particular mold.
What Are the Differences Between Vacuum Casting and Injection Molding?
The table below shows the differences, advantages, and disadvantages of vacuum casting and injection molding:
| Vacuum Casting | Injection Molding | |
| Commonly Used For | • Small quantities: Prototyping, bridge tooling, and small production runs. | • High volume production: Medium-to-large production runs. |
| Advantages | • Resins and silicone molds are cheap and manufacturing has a low cost. • Rapid tooling: Tooling lead times are faster since molds can easily be made using 3D printing or CNC machining and liquid silicone. |
• Highly automated process means the price per part is much lower compared to cast parts. • Large volumes of parts can be made in a short time. • Parts are ready to be used after molding. • Molds are durable and long-lasting since they are fabricated from hardened steel or aluminium. |
| Disadvantages | • Labour-intensive process which drives the price per part up. • Production output is small compared to injection molding. • Long production lead times. • Silicone molds are not as durable as metal molds. • Parts require post-processing and trimming after removal from the mold. |
• Long tooling lead times due to the extensive manufacturing processes needed to fabricate molds. • Expensive upfront costs. |
Summary
This article presented vacuum casting and injection molding, explained what they are, and discussed when to use each process best.
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities, including vacuum casting, injection molding, die casting, compression molding and other value-added services for all of your prototyping and production needs.
 Europe
Europe  Türkiye
Türkiye  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Global
Global 

 Login with my Xometry account
Login with my Xometry account  0
0








Comment(0)